Class NineSliceSprite
Hierarchy (View Summary)
- Sprite
- NineSliceSprite
Index
Constructors
Properties
Accessors
Methods
Constructors
constructor
- new NineSliceSprite(
x: number,
y: number,
settings: {
anchorPoint?: any;
flipX?: number;
flipY?: number;
frameheight?: number;
framewidth?: number;
height: number;
image: string | HTMLCanvasElement | HTMLImageElement | TextureAtlas;
insetx?: number;
insety?: number;
name?: string;
region?: string;
tint?: string | Color;
width: number;
},
): NineSliceSpriteParameters
- x: number
the x coordinates of the sprite object
- y: number
the y coordinates of the sprite object
- settings: {
anchorPoint?: any;
flipX?: number;
flipY?: number;
frameheight?: number;
framewidth?: number;
height: number;
image: string | HTMLCanvasElement | HTMLImageElement | TextureAtlas;
insetx?: number;
insety?: number;
name?: string;
region?: string;
tint?: string | Color;
width: number;
}Configuration parameters for the Sprite object
OptionalanchorPoint?: anyAnchor point to draw the frame at (defaults to the center of the frame).
OptionalflipX?: numberflip the sprite on the horizontal axis
OptionalflipY?: numberflip the sprite on the vertical axis
Optionalframeheight?: numberHeight of a single frame within the spritesheet
Optionalframewidth?: numberWidth of a single frame within the spritesheet
height: number
the height of the Renderable over which the sprite needs to be stretched
image: string | HTMLCanvasElement | HTMLImageElement | TextureAtlas
reference to spritesheet image, a texture atlas or to a texture atlas
Optionalinsetx?: numberthe width of a corner over which the sprite is unscaled (default is a quarter of the sprite width)
Optionalinsety?: numberthe height of a corner over which the sprite is unscaled (default is a quarter of the sprite height)
Optionalname?: stringname of this object
Optionalregion?: stringregion name of a specific region to use when using a texture atlas, see TextureAtlas
Optionaltint?: string | Colora tint to be applied to this sprite
width: number
the width of the Renderable over which the sprite needs to be stretched
Returns NineSliceSprite
- x: number
Properties
alpha
Define the renderable opacity
Set to zero if you do not wish an object to be drawn
always
Whether the renderable object will always update, even when outside of the viewport
ancestor
a reference to the parent object that contains this renderable
anchor
The anchor point is used for attachment behavior, and/or when applying transformations.
The coordinate system places the origin at the top left corner of the frame (0, 0) and (1, 1) means the bottom-right corner

a Renderable's anchor point defaults to (0.5,0.5), which corresponds to the center position.
Note: Object created through Tiled will have their anchorPoint set to (0, 0) to match Tiled Level editor implementation.
To specify a value through Tiled, use a json expression like json:{"x":0.5,"y":0.5}.
anim
animationpause
animationspeed
animation cycling speed (delay between frame in ms)
atlas
auto
When enabled, an object container will automatically apply any defined transformation before calling the child draw method.
Example
// enable "automatic" transformation when the object is activated
onActivateEvent: function () {
// reset the transformation matrix
this.currentTransform.identity();
// ensure the anchor point is the renderable center
this.anchorPoint.set(0.5, 0.5);
// enable auto transform
this.autoTransform = true;
....
}
blend
the blend mode to be applied to this renderable (see renderer setBlendMode for available blend mode)
body
the renderable physic body
Example
// define a new Player Class
class PlayerEntity extends me.Sprite {
// constructor
constructor(x, y, settings) {
// call the parent constructor
super(x, y , settings);
// define a basic walking animation
this.addAnimation("walk", [...]);
// define a standing animation (using the first frame)
this.addAnimation("stand", [...]);
// set the standing animation as default
this.setCurrentAnimation("stand");
// add a physic body
this.body = new me.Body(this);
// add a default collision shape
this.body.addShape(new me.Rect(0, 0, this.width, this.height));
// configure max speed, friction, and initial force to be applied
this.body.setMaxVelocity(3, 15);
this.body.setFriction(0.4, 0);
this.body.force.set(3, 0);
this.isKinematic = false;
// set the display to follow our position on both axis
me.game.viewport.follow(this.pos, me.game.viewport.AXIS.BOTH);
}
...
}
current
angle: number;
height: number;
idx: number;
length: number;
name: undefined;
offset: Vector2d;
width: number;
}
current
the renderable default transformation matrix
dt
edges
The edges here are the direction of the nth edge of the polygon, relative to
the nth point. If you want to draw a given edge from the edge value, you must
first translate to the position of the starting point.
floating
If true, this renderable will be rendered using screen coordinates, as opposed to world coordinates. Use this, for example, to define UI elements.
GUID
(G)ame (U)nique (Id)entifier"
a GUID will be allocated for any renderable object added
to an object container (including the me.game.world container)
image
indices
a list of indices for all vertices composing this polygon
insetx
insety
is
when true the renderable will be redrawn during the next update cycle
is
If true then physic collision and input events will not impact this renderable
is
make the renderable object persistent over level changes
is
true if this is a video sprite (e.g. a HTMLVideoElement was passed as as source)
mask
A mask limits rendering elements to the shape and position of the given mask object. So, if the renderable is larger than the mask, only the intersecting part of the renderable will be visible.
name
The name of the renderable
nss_
nss_
offset
global offset for the position to draw from on the source image.
on
an event handler that is called when the renderable leave or enter a camera viewport
points
Array of points defining the Polygon
Note: If you manually change points, you must call recalcafterwards so that the changes get applied correctly.
pos
origin point of the Polygon
reset
shader
(Experimental) an optional shader, to be used instead of the default built-in one, when drawing this renderable (WebGL only)
source
The source texture object this sprite object is using
texture
type
The shape type (used internally).
update
Whether to update this object when the game is paused.
Accessors
bottom
- get bottom(): number
bottom coordinate of the Rectangle
Returns number
center
- get centerX(): number
absolute center of this rectangle on the horizontal axis
Returns number
- set centerX(value: number): void
Parameters
- value: number
Returns void
center
- get centerY(): number
absolute center of this rectangle on the vertical axis
Returns number
- set centerY(value: number): void
Parameters
- value: number
Returns void
depth
- get depth(): number
the depth of this renderable on the z axis
Returns number
- set depth(value: number): void
Parameters
- value: number
Returns void
height
- get height(): number
height of the NineSliceSprite
Returns number
- set height(value: number): void
Parameters
- value: number
Returns void
in
- get inViewport(): boolean
- set inViewport(value: boolean): void
Parameters
- value: boolean
Returns void
is
- get isFlippedX(): boolean
is
- get isFlippedY(): boolean
is
- get isFloating(): boolean
left
- get left(): number
The left coordinate of the Rectangle.
Returns number
parent
returns the parent application (or game) to which this renderable is attached to
Returns Application
the parent application or undefined if not attached to any container/app
right
- get right(): number
right coordinate of the Rectangle
Returns number
tint
top
- get top(): number
top coordinate of the Rectangle
Returns number
width
- get width(): number
width of the NineSliceSprite
Returns number
- set width(value: number): void
Parameters
- value: number
Returns void
Methods
add
- addAnimation(
name: string,
index: string[] | number[] | object[],
animationspeed?: number,
): numberadd an animation
For fixed-sized cell sprite sheet, the index list must follow the logic as per the following example :

Parameters
- name: string
animation id
- index: string[] | number[] | object[]
list of sprite index or name defining the animation. Can also use objects to specify delay for each frame, see below
Optionalanimationspeed: numbercycling speed for animation in ms
Returns number
frame amount of frame added to the animation (delay between each frame).
Example
// walking animation
this.addAnimation("walk", [ 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 ]);
// standing animation
this.addAnimation("stand", [ 11, 12 ]);
// eating animation
this.addAnimation("eat", [ 6, 6 ]);
// rolling animation
this.addAnimation("roll", [ 7, 8, 9, 10 ]);
// slower animation
this.addAnimation("roll", [ 7, 8, 9, 10 ], 200);
// or get more specific with delay for each frame. Good solution instead of repeating:
this.addAnimation("turn", [{ name: 0, delay: 200 }, { name: 1, delay: 100 }])
// can do this with atlas values as well:
this.addAnimation("turn", [{ name: "turnone", delay: 200 }, { name: "turntwo", delay: 100 }])
// define an dying animation that stop on the last frame
this.addAnimation("die", [{ name: 3, delay: 200 }, { name: 4, delay: 100 }, { name: 5, delay: Infinity }])
// set the standing animation as default
this.setCurrentAnimation("stand"); - name: string
angle
return the angle to the specified target
Parameters
- target: any
Returns number
angle in radians
center
center the rectangle position around the given coordinates
Parameters
- x: number
the x coordinate around which to center this rectangle
- y: number
the y coordinate around which to center this rectangle
Returns NineSliceSprite
this rectangle
- x: number
clone
contains
Returns true if the polygon contains the given point.
(Note: it is highly recommended to first do a hit test on the corresponding
bounding rect, as the function can be highly consuming with complex shapes)Parameters
- x: number
x coordinate or a vector point to check
- y: number
y coordinate
Returns boolean
True if the polygon contain the point, otherwise false
- x: number
Returns true if the polygon contains the given point.
(Note: it is highly recommended to first do a hit test on the corresponding
bounding rect, as the function can be highly consuming with complex shapes)Parameters
- vector: Vector2d
Returns boolean
True if the polygon contain the point, otherwise false
contains
Returns true if the rectangle contains the given rectangle
Parameters
- rectangle: Rect
rectangle to test
Returns boolean
True if the rectangle contain the given rectangle, otherwise false
- rectangle: Rect
copy
copy the position and size of the given rectangle into this one
Parameters
- rect: Rect
Source rectangle
Returns NineSliceSprite
new rectangle
- rect: Rect
distance
return the distance to the specified target
Parameters
- target: any
Returns number
distance
equals
Check if this rectangle is identical to the specified one.
Parameters
- rect: Rect
Other rectangle.
Returns boolean
true if equals
- rect: Rect
flicker
make the object flicker
Parameters
- duration: number
expressed in milliseconds
Optionalcallback: Function = undefinedFunction to call when flickering ends
Returns Sprite
Reference to this object for method chaining
- duration: number
flip
flip the renderable on the horizontal axis (around the center of the renderable)
Parameters
Optionalflip: boolean = truetrueto flip this renderable.
Returns Renderable
Reference to this object for method chaining
flip
flip the renderable on the vertical axis (around the center of the renderable)
Parameters
Optionalflip: boolean = truetrueto flip this renderable.
Returns Renderable
Reference to this object for method chaining
get
return the renderable absolute position in the game world
Returns Vector2d
get
get
return the current animation frame index.
Returns number
current animation frame index
get
returns a list of indices for all triangles defined in this polygon
Returns number[]
an array of vertex indices for all triangles forming this polygon.
get
get the renderable alpha channel value
Returns number
current opacity value between 0 and 1
is
Returns true if the vertices composing this polygon form a convex shape (vertices must be in clockwise order).
Returns boolean | null
true if the vertices are convex, false if not, null if not computable
is
is
Determines whether all coordinates of this rectangle are finite numbers.
Returns boolean
false if all coordinates are positive or negative Infinity or NaN; otherwise, true.
is
return the flickering state of the object
Returns boolean
look
Rotate this renderable towards the given target.
Parameters
- target: any
the renderable or position to look at
Returns Renderable
Reference to this object for method chaining
- target: any
on
onCollision callback, triggered in case of collision, when this renderable body is colliding with another one
Returns boolean
true if the object should respond to the collision (its position and velocity will be corrected)
Example
// colision handler
onCollision(response) {
if (response.b.body.collisionType === me.collision.types.ENEMY_OBJECT) {
// makes the other object solid, by substracting the overlap vector to the current position
this.pos.sub(response.overlapV);
this.hurt();
// not solid
return false;
}
// Make the object solid
return true;
},
on
OnDestroy Notification function
Called by engine before deleting the objectReturns void
overlaps
check if this rectangle is intersecting with the specified one
Parameters
- rect: Rect
Other rectangle.
Returns boolean
true if overlaps
- rect: Rect
pause
play or resume the current animation or video
Returns void
play
play or resume the current animation or video
Returns void
post
restore the rendering context after drawing (automatically called by melonJS).
Parameters
- renderer: CanvasRenderer | WebGLRenderer
a renderer object
Returns void
- renderer: CanvasRenderer | WebGLRenderer
pre
Prepare the rendering context before drawing (automatically called by melonJS). This will apply any defined transforms, anchor point, tint or blend mode and translate the context accordingly to this renderable position.
Parameters
- renderer: CanvasRenderer | WebGLRenderer
a renderer object
Returns void
- renderer: CanvasRenderer | WebGLRenderer
recalc
Computes the calculated collision polygon. This must be called if the
pointsarray,angle, oroffsetis modified manually.Returns NineSliceSprite
Reference to this object for method chaining
resize
resize the rectangle
Parameters
- w: number
new width of the rectangle
- h: number
new height of the rectangle
Returns NineSliceSprite
this rectangle
- w: number
reverse
reverse the given or current animation if none is specified
Parameters
Optionalname: stringanimation id
Returns Sprite
Reference to this object for method chaining
rotate
Rotate this renderable by the specified angle (in radians).
Parameters
- angle: number
The angle to rotate (in radians)
Optionalv: anyan optional point to rotate around
Returns Renderable
Reference to this object for method chaining
- angle: number
scale
scale the renderable around his anchor point. Scaling actually applies changes to the currentTransform member wich is used by the renderer to scale the object when rendering. It does not scale the object itself. For example if the renderable is an image, the image.width and image.height properties are unaltered but the currentTransform member will be changed.
Parameters
- x: number
a number representing the abscissa of the scaling vector.
Optionaly: number = xa number representing the ordinate of the scaling vector.
Returns Renderable
Reference to this object for method chaining
- x: number
scale
scale the renderable around his anchor point
Parameters
- v: Vector2d
scaling vector
Returns Renderable
Reference to this object for method chaining
- v: Vector2d
set
force the current animation frame index.
Parameters
Optionalindex: number = 0animation frame index
Returns Sprite
Reference to this object for method chaining
set
set the current animation this will always change the animation & set the frame to zero
Parameters
- name: string
animation id
OptionalresetAnim: string | Functionanimation id to switch to when complete, or callback
Optionalpreserve_dt: boolean = falseif false will reset the elapsed time counter since last frame
Returns Sprite
Reference to this object for method chaining
Example
// set "walk" animation
this.setCurrentAnimation("walk");
// set "walk" animation if it is not the current animation
if (this.isCurrentAnimation("walk")) {
this.setCurrentAnimation("walk");
}
// set "eat" animation, and switch to "walk" when complete
this.setCurrentAnimation("eat", "walk");
// set "die" animation, and remove the object when finished
this.setCurrentAnimation("die", () => {
world.removeChild(this);
return false; // do not reset to first frame
});
// set "attack" animation, and pause for a short duration
this.setCurrentAnimation("die", () => {
this.animationpause = true;
// back to "standing" animation after 1 second
setTimeout(function () {
this.setCurrentAnimation("standing");
}, 1000);
return false; // do not reset to first frame
});- name: string
set
set the renderable alpha channel value
Parameters
- alpha: number
opacity value between 0.0 and 1.0
Returns void
- alpha: number
set
change the current texture atlas region for this sprite
Parameters
- region: object
typically returned through me.Texture.getRegion()
Returns Sprite
Reference to this object for method chaining
- region: object
set
set new value to the Polygon
Parameters
- x: number
position of the Polygon
- y: number
position of the Polygon
- points: PolygonVertices | LineVertices
array of vector or vertice defining the Polygon
Returns NineSliceSprite
this instance for objecf chaining
- x: number
set
Set new dimensions for the rectangle.
Parameters
- width: number
The new width of the rectangle.
- height: number
The new height of the rectangle.
Returns NineSliceSprite
- width: number
set
set the vertices defining this Polygon
Parameters
- vertices: PolygonVertices | LineVertices
array of vector or vertice defining the Polygon
Returns NineSliceSprite
this instance for objecf chaining
- vertices: PolygonVertices | LineVertices
shift
to2d
apply a 2d projection to this shapen
Returns NineSliceSprite
Reference to this object for method chaining
to
apply an isometric projection to this shape
Returns NineSliceSprite
Reference to this object for method chaining
to
Returns a polygon whose edges are the same as this box.
Returns Polygon
a new Polygon that represents this rectangle.
transform
multiply the renderable currentTransform with the given matrix
Parameters
- m: Matrix2d
the transformation matrix
Returns Renderable
Reference to this object for method chaining
- m: Matrix2d
translate
Translates the Polygon by the specified offset.
Parameters
- x: number
The x offset or a vector point to translate by.
Optionaly: numberThe y offset. This parameter is required if the first parameter is a number.
Returns Polygon
Reference to this object for method chaining
- x: number
union
merge this rectangle with another one
Parameters
- rect: Rect
other rectangle to union with
Returns NineSliceSprite
the union(ed) rectangle
- rect: Rect
Protectedupdate
Protectedupdate function.
automatically called by the game manager gameParameters
- dt: number
time since the last update in milliseconds.
Returns boolean
true if the Sprite is dirty
- dt: number
update
update the bounding box for this shape.
Parameters
Optionalabsolute: boolean = trueupdate the bounds size and position in (world) absolute coordinates
Returns Bounds
this shape bounding box Rectangle object
A NineSliceSprite is similar to a Sprite, but it uses 9-slice scaling to strech its inner area to fit the size of the Renderable, by proportionally scaling a sprite by splitting it in a grid of nine parts (with only parts 1, 3, 7, 9 not being scaled).
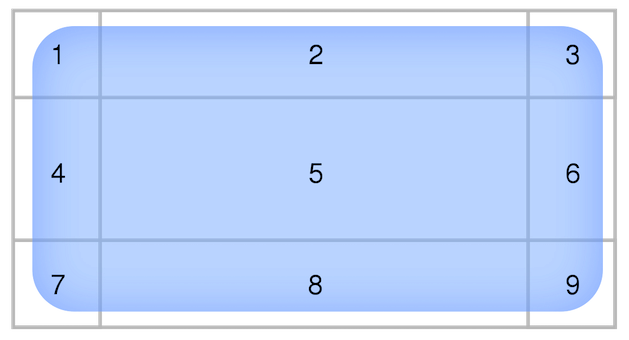
See
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/9-slice_scaling